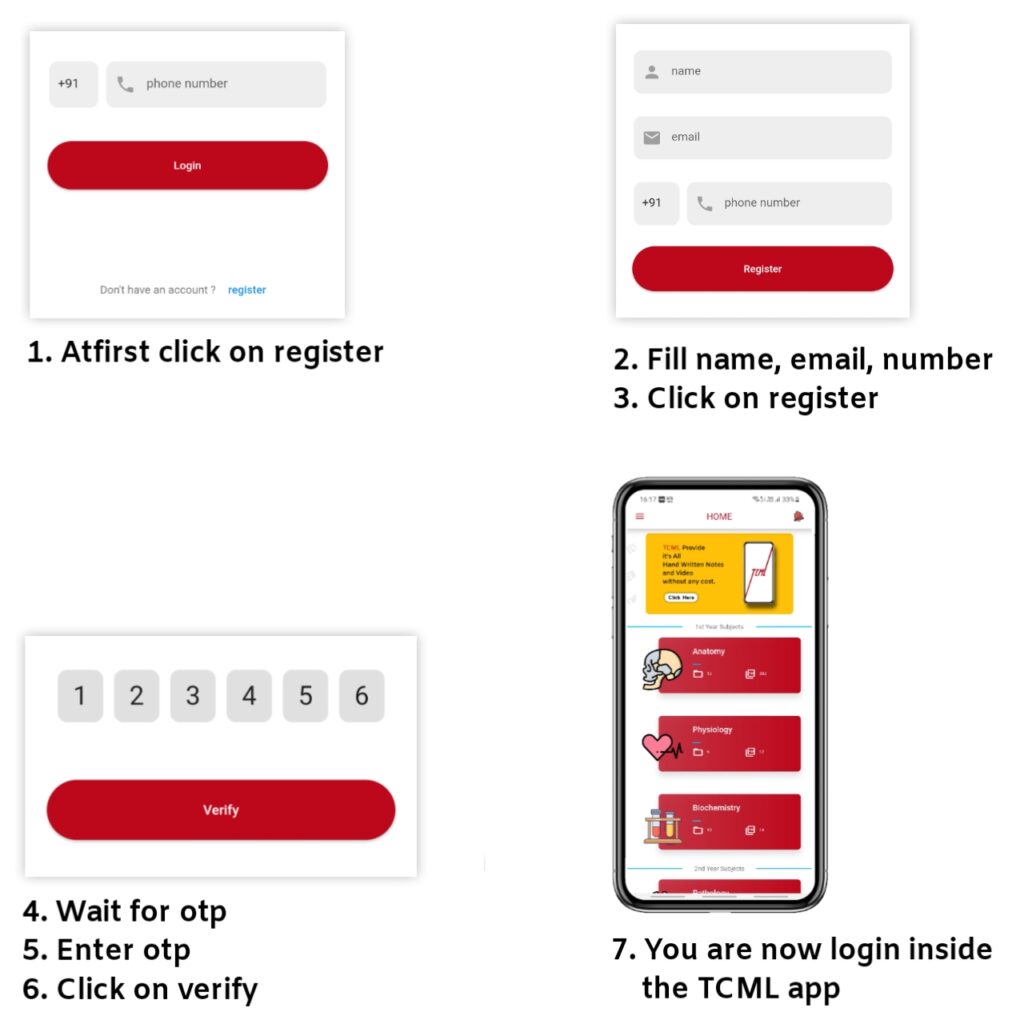
What is GERD?
Due to Reflux of gastric content/content from stomach to esophagus.
Cause of GERD-
Due to decrease lower esophageal sphincter (LES) tone, LES is not properly closed, as result gastric content reflux into esophagus and damage the mucosa of esophagus. (See Treatmentof GERD – Prokinetic drug)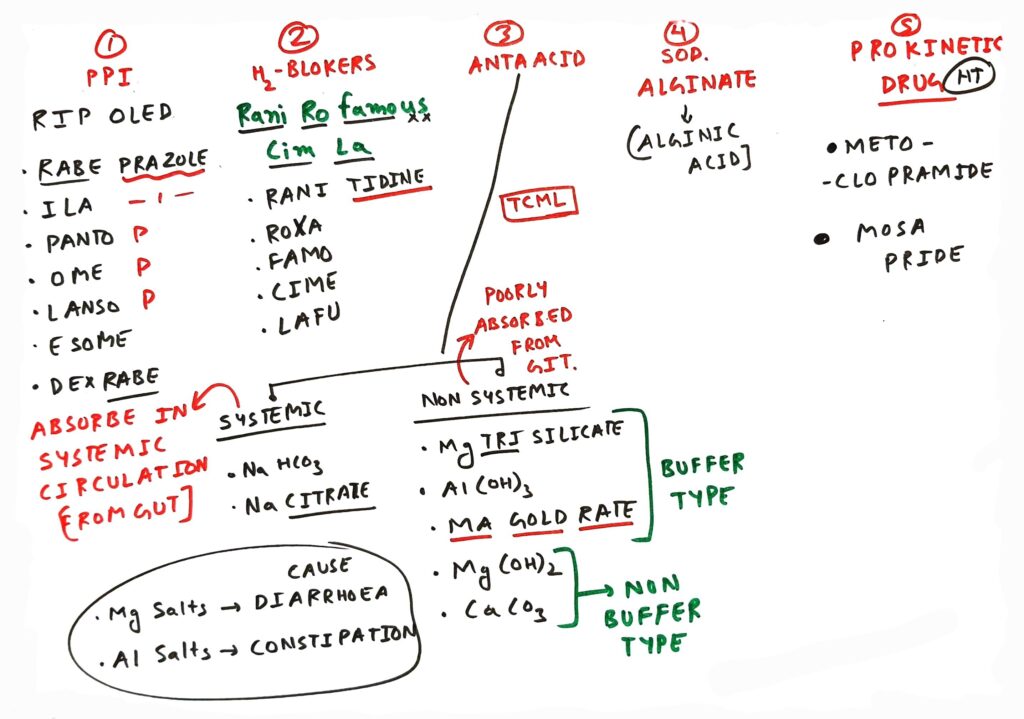
Treatment of GERD –
1. PPI (Proton pump inhibitor) :
MOA (Mechanism of action) – Inhibit gastric acid secretion
eg. Pantoprazole, rabeprazole
2. H2 blocker :
MOA – Inhibit gastric acid secretion
eg. Ranitidine
3. Antacid :
MOA – Neutralize gastric acid
eg. Sodium bicarbonate
4. Sodium aliginate :
MOA –
• These drug Increase viscosity of gastric content viscosity
• It floats on the surface, As a result gastric acid could not have direct contact with esophageal mucosa
eg. Alginic acid
5. Prokinetic drug :
MOA –
• These drug Increase lower esophageal sphincter tone as result gastric content reflux into esophagus and damage the mucosa of esophagus. (See cause of GERD)
• Increase gastric empty
eg. Metoclopramide
Reference-
1. Sharma & Sharma’s, Principles of Pharmacology, 3rd Edition
2. KD Tripathi, Essentials of medical Pharmacology, 8th Edition
3. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, South asia edition, Volume 2