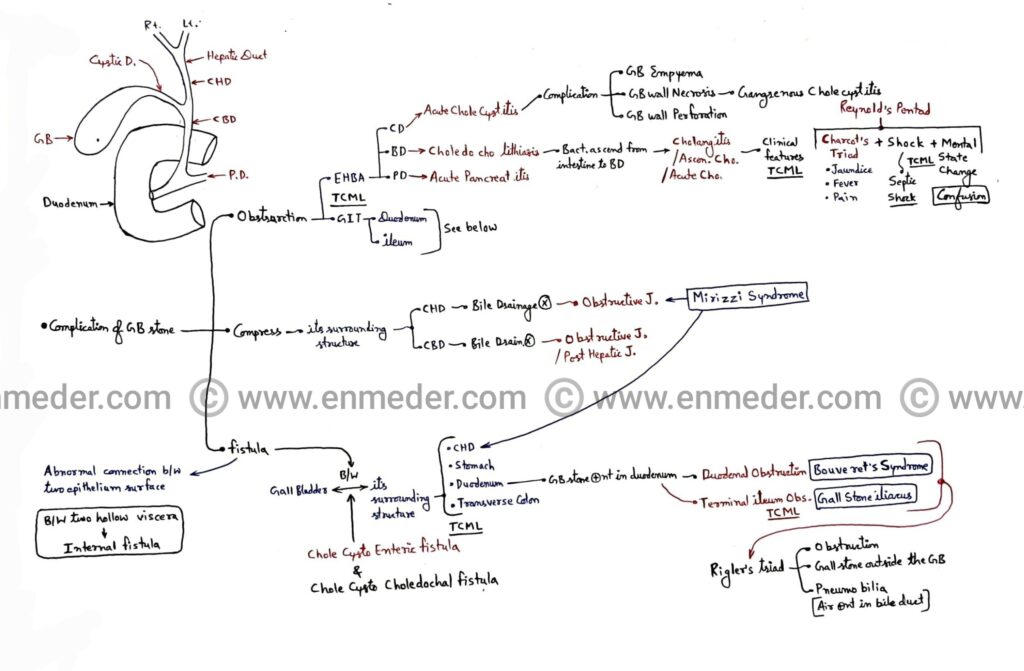
Complications of gallstone/cholelithiasis-
1. Obstruction of extra hepatic biliary apparatus and gastrointestinal tract
2. Compression of common hepatic duct and common bile duct
3. Fistula between gallbladder and it’s surrounding structures
1. Obstruction –
A. Extra hepatic biliary apparatus (EHBA) –
1. Cystic duct (CD)
Due to obstruction of cystic duct by gallstone it causes acute cholecystitis, gallbladder empyema, gangrenous cholecystitis, gallbladder wall perforation.
2. Bile duct (BD)
Due to obsruction of bile duct by gallstone it causes choledocholithiasis, cholangitis (ascending Cholangitis).
NOTE – Clinical features of cholangitis
Charcot’s triad – Obstruction jaundice, pain, and fever
Reynold’s pentad – It includes charcot’s triad, septic shock and mental status change (confusion).
3. Pancreatic duct (PD)
Due to obsruction of bile duct by gallstone it cause acute pancreatitis.
B. Gastrointestinal tract –
1. Duodenum obstruction
2. ileum obstruction
For more detail see fistula
2. Compression –
Gallbladder stone also compress it’s structures (Common hepatic duct and common bile duct) and cause obstruction jaundice.
NOTE – Mirizzi Syndrome
Gallstone compress the common hepatic duct (CHD) and cause obstructive jaundice.
If the compression is lasts for a long time, it can become a fistula too.
3. Fistula –
1. Fistula is a abnormal connection between two epithelium surface.
2. It the case of gallbladder stone fistula present between gallbladder and it’s surrounding structures such as common hepatic duct, stomach, duodenum, transverse colon.
3. Cholecysto enteric fistula – Fistula between gallbladder and gastrointestinal tract.
Bouvenet’s syndrome – Due to cholecysto enteric fistula gallstone move from gallbladder to duodenum and cause duodenal obstruction.
4. Cholecysto choledochal fistula – Fistula between gallbladder and common hepatic duct.
Gallstone iliacus – It is due to cholecysto enteric fistula gallstone move from gallbladder to duodenum and then obstruct terminal part of ileum.
5. Rigler’s triad
1. Obstructive
2. Gallstone outside from the gallbladder
3. Pneumobilia – air present in bile duct
🔴 Now all TCML hand written notes and charts are available on TCML Mobile App (FREE for all users).
To download TCML Mobile App click on below pic.