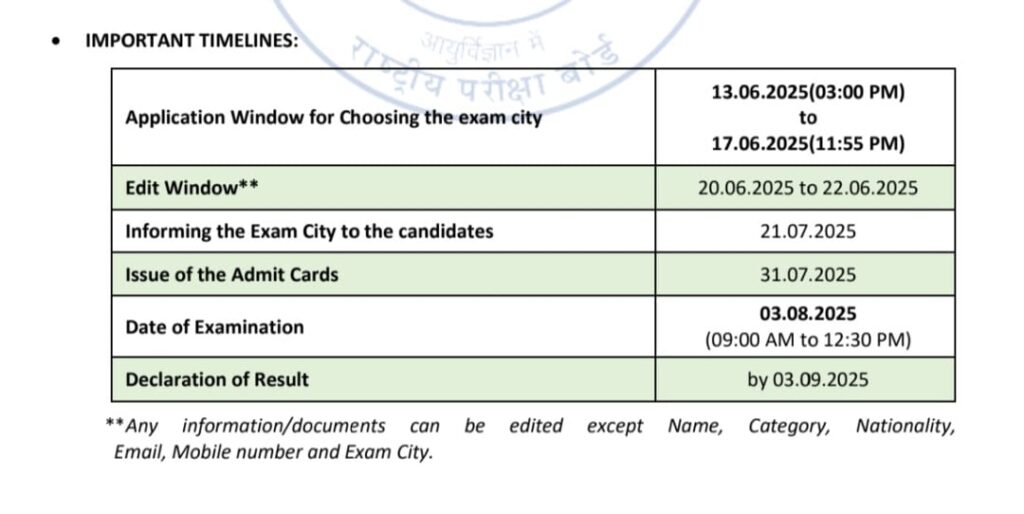
URGENT NEET PG 2025 Candidates Must Re-Choose Exam Centers – Complete Timeline
🚨 URGENT: NEET PG 2025 Exam Center Re-Selection Required ⚠️ IMMEDIATE ACTION REQUIRED All NEET PG 2025 candidates must re-submit their exam center preferences 📢 Official Notice from NBEMS – June 7, 2025 The National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS) has announced that NEET PG 2025 will be conducted in a single shift […]
URGENT NEET PG 2025 Candidates Must Re-Choose Exam Centers – Complete Timeline Read More »