neet pg
Femoral triangle, sheath and canal
Chart Highlights- 1. Femoral triangle 2. Femoral sheath – It is divided into three compartment (Lateral, intermediate and lateral)3. Femoral canal – It is the medial compartment of femoral sheath.4. Femoral ring – It is the base of femoral canal.
Femoral triangle, sheath and canal Read More »
Shoulder joint
Chart Highlights- 1. Shoulder joint relation 2. Coraco acromial arch 3. Musculo tendinious cuff 4. Bicipital groove 5. Axillary artery (1st rib, pectoralis minor, and teres major)
Elbow joint
Chart Highlights- 1. Coronoid process 2. Coronoid fossa 3. Coranoid process 4. Olecranon process 5. Olecranon fossa 6. Trochlear notch 7. Trochlea 8. Radial notch 9. Radial fossa
Allen’s test
It is perform to examine the artery patency. Hand blood supply- 1. Superficial palmar arch 2. Deep palmar arch
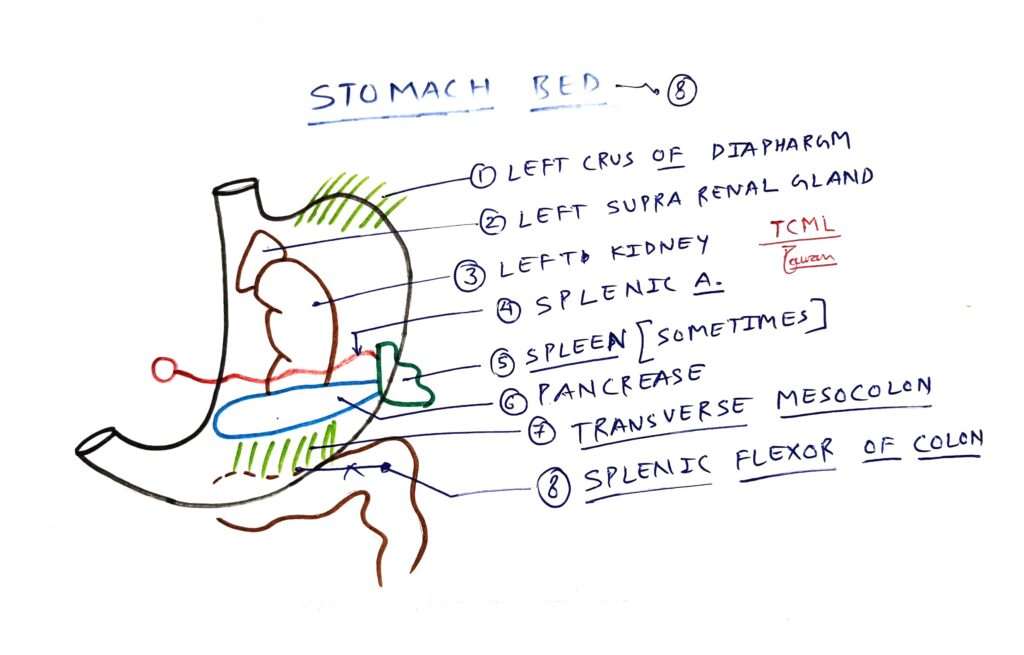
Stomach bed
Chart Overview- A. Stomach bedB. Stomach posterior relation Stomach bed is also called posterior relation of stomach because structures that form stomach bed are present posterior side of stomach. Total eight structures form the stomach bed which is given below. 1. Diaphragm (left crus)2. Suprarenal gland (Left side)3. Kidney (Left side)4. Splenic artery (It is
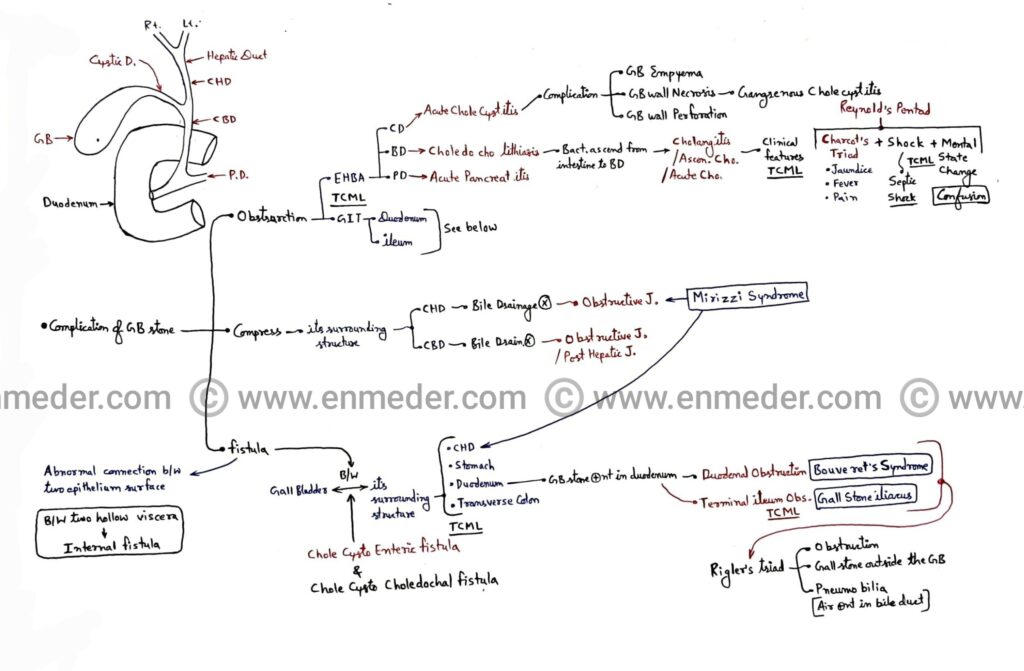
GallBladder stone
Complications of gallstone/cholelithiasis- 1. Obstruction of extra hepatic biliary apparatus and gastrointestinal tract 2. Compression of common hepatic duct and common bile duct 3. Fistula between gallbladder and it’s surrounding structures 1. Obstruction – A. Extra hepatic biliary apparatus (EHBA) – 1. Cystic duct (CD)Due to obstruction of cystic duct by gallstone it causes acute
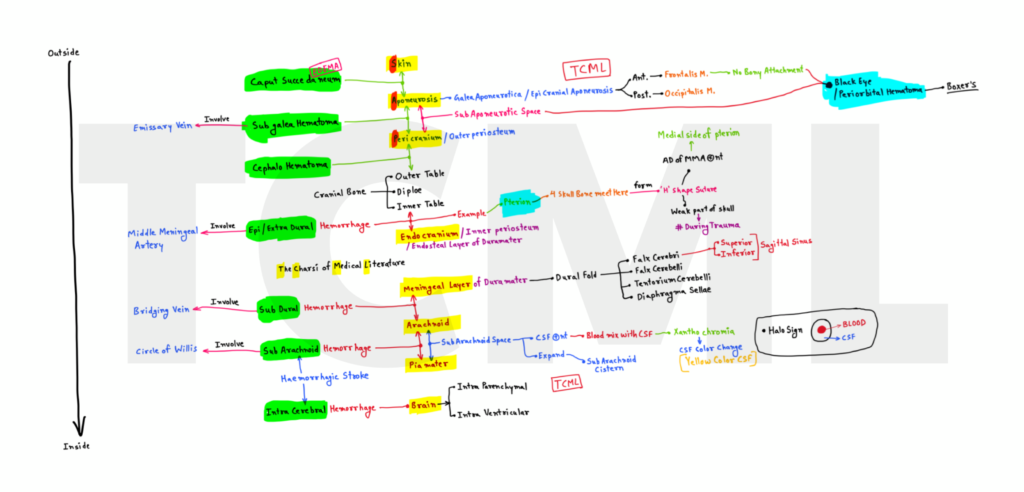
Intracranial hemorrhage
Overview – 1. SCALP layer’s 2. Meninges 3. Extra cranial or SCALP haemorrhage 4. Intra cranial hemorrhage 5. Cause Download here Layers from outside to inside – 1. Skin 2. Connective tissue 3. Aponeurosis or epicranial aponeurosis or galea aponeurotica 4. Loose connective tissue / Sub aponeurotic space 5. Pericardium / Outer periosteum 6. Outer
Intracranial hemorrhage Read More »